STREAM AND FILES-II
Reader
and Writer classes
Reader
Reader
is an abstract class that defines java's model of streaming character input.
All of the methods in this class will throw an IOException on error condition.
File Reader
The
FileReader class creates a Reader that you can use to read the content of a
file. its two most commonly used constructors are shown here
FileReader(Stringfile Path)
FileReader(Filefile Obj)
EXAMPLE:1
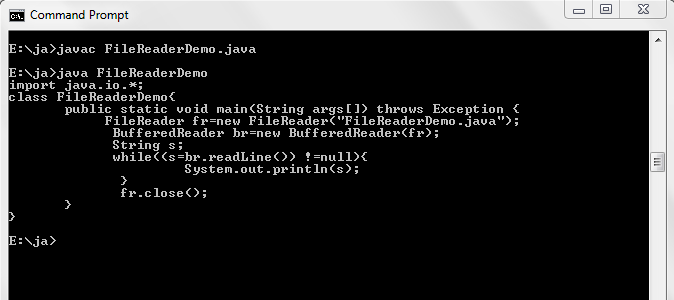
File name: FileReaderDemo.java
import java.io.*;
class FileReaderDemo{
public static void main(String args[])
throws Exception {
FileReader fr=new
FileReader("FileReaderDemo.java");
BufferedReader br=new
BufferedReader(fr);
String s;
while((s=br.readLine()) !=null){
System.out.println(s);
}
fr.close();
}
}
Output
File Writer
FileWriter creates a writer that you can use to write to a file.its most commonly used
constructors are shown here
FileWriter(Stringfile Path)
FileWriter(Stringfile Path,boolean
append)
FileWriter(File fileObj)
Example : 2
// Demonstrate FileWriter.
File name: FileWriterDemo.java
import java.io.*;
class FileWriterDemo{
public static void main(String
args[]) throws Exception{
String source="Now is the time for all
good men\n"+" to come to the aid of their country\n"
+" and paid their due taxes.";
char buffer[]=new char[source.length()];
source.getChars(0,source.length(),buffer,0);
FileWriter f1=new FileWriter("file1.txt");
for(int
i=0;i<buffer.length;i+=1){
f1.write(buffer[i]);
}
f1.close();
FileWriter f2=new
FileWriter("file2.txt");
f2.write(buffer);
f2.close();
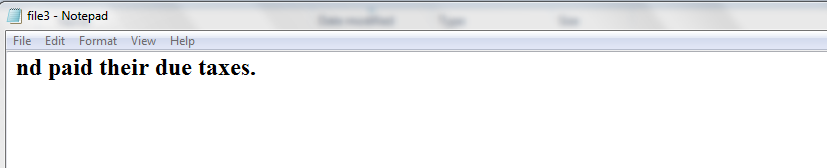
FileWriter f3=new
FileWriter("file3.txt");
f3.write(buffer,buffer.length-buffer.length/4,buffer.length/4);
f3.close();
}
}
Output
CharArrayReader
CharArrayReader is an implementation of an input stream that
uses a character array as the source.To provide the data source:
CharArrayReader(char array[])
CharArrayReader(char array[],intstart,intnumChars)
EXAMPLE : 3
// Demonstrate CharArrayReader.
import java.io.*;
public class CharArrayReaderDemo
{
public static void main(String
args[]) throws IOException
{
String
temp="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
int length=temp.length();
char c[]=new char[length];
temp.getChars(0,length,c,0);
CharArrayReader input1=new
CharArrayReader(c);
CharArrayReader input2=new
CharArrayReader(c,0,5);
int I;
System.out.println("inputl is:");
while((I=input1.read()) !=-1){
System.out.print((char)I);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("input2
is:");
while((I=input2.read()) !=-1){
System.out.print((char)I);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Output
CharArrayWriter
CharArrayWriter is an implementation of an output stream
that uses an array as the destination.CharArrayWriter has two
constructors,shown here:
CharArrayWriter()
CharArrayWriter(int numChars)
EXAMPLE :4
File name:
CharArrayWriterDemo.java
import java.io.*;
class CharArrayWriterDemo{
public static void main(String
args[]) throws IOException{
CharArrayWriter f=new
CharArrayWriter();
String s="This should end up
in the array";
char buf[]=new char[s.length()];
s.getChars(0,s.length(),buf,0);
f.write(buf);
System.out.println("Buffer as
a string");
System.out.println(f.toString());
System.out.println("Into
array");
char c[]=f.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++){
System.out.print(c[i]);
}
System.out.println("\nTo a
FileWriter()");
FileWriter f2=new
FileWriter("test.txt");
f.writeTo(f2);
f2.close();
System.out.println("Doing a
reset");
f.reset();
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
f.write('X');
System.out.println(f.toString());
}
}
Output
BufferedReader
BufferedReader improves performance by buffering input. it
has two constructors:
BufferedReader(Reader inputStream)
BufferedReader(Reader inputStream,int
bufSize)
EXAMPLE :5
File name: BRReadLines.java
import java.io.*;
class BRReadLines{
public static void main(String
args[]) throws IOException
{
// create a
BufferedReader using System.in
BufferedReader br=
new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str;
System.out.println("Enter
lines of text.");
System.out.println("Enter
'stop' to quit.");
do {
str=br.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
}while(!str.equals("stop"));
}
}
Output
BufferedWriter
a BufferedWriter
is an Writer that adds a flush() method that can be used to ensure that data
buffers are physically written to the actual output stream. using a
BufferedWriter can increase performance by reducing the number of times data is
actually physically written to the output stream
A BufferedWriter has these two constructors:
BufferedWriter(Writer outputStream)
BufferedWriter(Writer outputStream,int
bufSize)
PrintWriter
PrintWriter is essentially a character-oriented version of Print Stream .
it provides the formatted output methods print() andprintln().PrintWriter has
four constructors:
PrintWriter(OutputStream outputStream)
PrintWriter(OutputStream outputStream,boolean
flushOnNewline)
PrintWriter(Writer outputStream)
PrintWriter(Writer outputStream, boolean
flushOnNewline)
EXAMPLE :6
//Demonstrate PrintWriter
File name: PrintWriterDemo.java
import java.io.*;
public class PrintWriterDemo{
public static void main(String
args[]){
PrintWriter pw = new
PrintWriter(System.out,true);
pw.println("This is a
string");
int i=-7;
pw.println(i);
double d = 4.5e-7;
pw.println(d);
}
}
Output










0 comments:
Post a Comment