2 CHAPTER: DATA TYPES
*Integers - This group includes byte,
short, int and long, which are for whole value designed numbers.
*Floating-point
numbers- This group includes float and double, which represent numbers with
fractional precision.
*Characters
- This group includes char, which represents symbols in a character set, like
letters and numbers.
*Boolean
- This group includes boolean, which is a special type for representing
true/false values.
// Compute no of seconds in 100 years.
File name : IntegerDemo.java
class IntegerDemo{
public static void main (String args[]){
int years;
int days;
long nodays;
long seconds;
years = 100;
days = 365;
nodays=years * days;
seconds =
nodays*24*60*60;
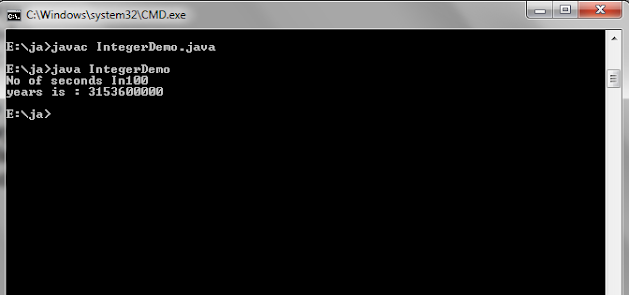
System.out. println("No of seconds
In"+years);
System.out.println("years is :
"+seconds);
}
}
Output
FLOAT:
Floating
- point numbers are used for numbers with a decimal part. There are two
floating-point types:float (32 bits, single-precision)and double
(64bits,double-precision).
Type Size Range
double 64bits 1.7e-308to1.7e+308
float 32bits 3.4e-038to3.4e+038
//Compute the area of a circle.
File name:DoubleDemo.java
class DoubleDemo{
public static void main (String args[]){
double a;
float r=10.8f,pi=3.1416f;
a=pi*r*r;
System.out.println("Area of circle is"+a);
}
}
output:
Character:
The char
type is used for individual characters. Because java uses the Unicode character
set, the type has 16 bits of precision,unsigned.
//Demonstrate char data type.
File name:CharDemo.java
class CharDemo{
public static void main (String args[]){
char ch1,ch2;
ch1=65;
ch2=ch1;
ch2++;
System.out.print("ch1 and ch2:");
System.out.println(ch1+"
"+ch2);
}
}
output:
Boolean:
Boolean
type can have one of two values, true of false. Note that unlike in other C
like languages, boolean is not a number, nor can it be treated as one. All tests
of boolean variables should test for true or false.
//Demonstrate boolean values.
File name: BooleanDemo.java
class BooleanDemo{
public static void main (String args[]){
boolean b;
int x,y;
b=false;
x=30;
y=20;
b=x>y;
System.out.println("x is greater than y:"+b);
}
}
output:
Example:
File name: VarDeclaDemo.java
class VarDeclaDemo
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int a=70;
short b=2;
float c=12.57f;
String name="Samuel";
System.out.println("The integer
value is"+a);
System.out.println("The integer
value is"+b);
System.out.println("The integer
value is"+c);
System.out.println("The string
value is"+ name);
}
}
The output appears as
given below:
The Scope of Variables
File name: ScopeDemo.java
class ScopeDemo{
public static void main (String args[]){
int x; //Known to all code within main
x=10;
{ //start new scope
int y=20; //known only to this block
//x and y both known
here.
System.out.println("X="+x+" Y="+y);
}
//x is still known here.
System.out.println("x is "+x);
}
}
Output
Type Conversion and Casting
Converting one data Type into another data type is called Type Conversion.
File name: ConversionDemo.java
class ConversionDemo{
public static void main (String args[]){
byte b;
int i= 257;
System.out.println("\nConversion of int to byte.");
b=(byte)i;
System.out.println("i ="+i+" and b="+b);
}
}
This program generates the following output:







0 comments:
Post a Comment