Inheritance
one object
acquires properties & behaviour of parent class
Advantages
of Inheritance:
] Reusability of code.
] It can be used to create new subclasses.
] It saves time and effort.
Inheritance
Basics
To
inherit a class , the definition of one class into another by using the keyword
extends.
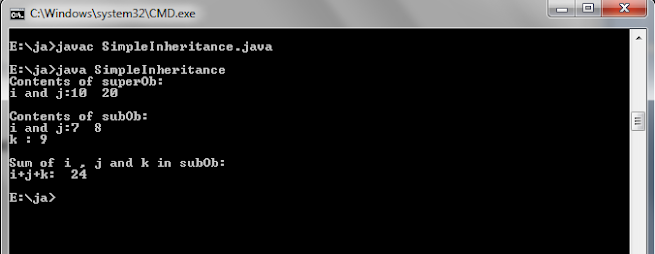
// A simple example of inheritance.
//
Create a superclass.
File name: A.java
class A{
int i, j;
void showij(){
System.out.println("i and j:"+i+" "+j);
}
}
//
Create a subclass by extending class A.
File
name: B.java
class B extends A{
int k;
void showk() {
System.out.println("k : "+k);
}
void sum() {
System.out.println("i+j+k:
"+(i+j+k));
}
}
File
name: SimpleInheritance.java
class
SimpleInheritance{
public static void
main(String args[]){
A superOb=new A();
B subOb=new B();
//The superclass may be used by itself.
superOb.i=10;
superOb.j=20;
System.out.println("Contents of
superOb:");
superOb.showij();
System.out.println();
/*The subclass has access to all public members fits superclass.*/
subOb.i=7;
subOb.j=8;
subOb.k=9;
System.out.println("Contents of
subOb:");
subOb.showij();
subOb.showk();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Sum of i , j and k
in subOb:");
subOb.sum();
}
}
Output
Member Access and
Inheritance
Although a subclass includes all of the members of its
superclass ,it cannot access those member of the superclass that have been
declared as private.
/*In a class
hierarchy, private members remain
private to
their class. This program contains as error and will not compile.
*/
//Create
a superclass.
File
name:
Ainheritance.java
class Ainheritance {
int i;// public by default
private int j; // private to A
void setij(int x, int y) {
i = x;
j = y;
}
}
//
A's j is not accessible here.
File
name:
Binheritance
class Binheritance extends Ainheritance {
int
total ;
void
sum() {
total=i+j; //ERROR,j is not accessible here
}
}
File
name:
Access.java
class Access{
public
static void main(String args[]) {
Binheritance subOb=new Binheritance();
subOb.setij(10,12);
subOb.sum();
System.out.println("Total
"+ subOb.total);
}
}
Output
Using super
Subclass needs to refer to its immediate superclass
, use the keyword super.
Super
super(parameter-list);
/*
programe to illustrate single inheritance*/
File
name: Book.java
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Book
{
int bno;
String
bname;
double
price;
public
Book(int n,String bn,double p)
{
bno=n;
bname=bn;
price=p;
}
void
display()
{
System.out.println("\nBook Number = " + bno);
System.out.println("\nBook Number = " + bname);
System.out.println("\nBook Number = " + price);
}
}
File
name:
Purchase.java
class Purchase extends Book
{
int qord;
double
netcost;
public
Purchase(int n1,String bn1, double p1,int q)
{
super(n1,bn1,p1); //Base Class Constructor
qord=q;
}
void
display() //Overriding of methods
{
netcost=qord*super.price; //Baseclass Variable
super.display(); //Base class
Function
System.out.println("\nQuantity ordered = "+qord);
System.out.println("\nNet cost="+netcost);
}
}
File
name: Inherit1.java
class Inherit1
{
public
static void main(String args[])
{
Purchase
pur =new Purchase(10,"Black book of java",500.00,34);
pur.display();
}
}
Output
Method overiding and Hierarchical
Inheritance
//Using run-time polymorphism.
File name: Figure.java
class Figure{
double dim1;
double dim2;
Figure(double a,
double b) {
dim1
=a;
dim2
=b;
}
double area() {
System.out.println("Area for Figure is undefined.");
return 0;
}
}
File name: Rectangle.java
class Rectangle extends Figure {
Rectangle(double
a,double b) {
super(a,b);
}
// override area
for rectangle
double area() {
System.out.println("Inside
Area for Rectangle.");
return dim1*
dim2;
}
}
File name: Triangle.java
class Triangle extends Figure {
Triangle(double
a, double b) {
super(a,
b);
}
//override area
for right triangle
double area() {
System.out.println("Inside Area for Triangle.");
return dim1 *
dim2/ 2;
}
}
File name: FindAreas.java
class FindAreas{
public static
void main(String args[]) {
Figure f =new
Figure(10, 10);
Rectangle r
=new Rectangle(9,5);
Triangle t =
new Triangle(10, 8);
Figure figref;
figref = r;
System.out.println("Area is" + figref.area());
figref = t;
System.out.println("Area is" + figref.area());
figref = f;
System.out.println("Area is" + figref.area());
}
}
Output
Using Final
To disallow a method from being overridden, specify
final as a modifier at the start of its declaration.
Example
class A {
final void meth() {
System.out.println("This is a final method.");
}
}
class B extends A {
void meth() {//ERROR
can't override.
System.out.printIn("ILLegal!");
}
}




0 comments:
Post a Comment