NetWorking(URL
, SOCKET(TCP/IP),DATAGRAMS)- II
Datagrams
Datagrams are bundles of information passed between machines.
java implements Datagrams on top of the UDP protocol by using two classes. The Datagrams Packet
object is the data container,while the Datagrams Socket is the mechanism used
to send or receive the Datagram Packets.
Datagrampacket
Datagrampacket defines several
constructors.
Datagrampacket(byte data[],int size)
Datagrampacket(byte data[],int offset,int size)
Datagrampacket(byte data[],int size,InetAddress ipAddress,int
port)
Datagrampacket(byte data[],int offset,int size,Inet Address
ipAddress,int port)
The first constructor specifies a buffer that will receive data,and the
size of a packet.it is used for receiving data over a Datagramsocket.The second
form allows you to specify an offset into the buffer at which data will be
stored.the third form specifies a target address and port,which are used by a
Datagramsocket to determine where the data in the packet will be sent. the fourth form transmit packets beginning at
the specified offset into the data.
InetAddress getAddress( )-> Returns the destination
InetAddress,typically used for sending.
int getport( )->Returns the port number.
byte[]getdata( )->Return the byte array of data contained in the
datagram .mostly used to retrieve data from the datagram after it has been
received.
int getLength( )->Return the length of the valid contained inthe byte
array that would be returned from the getdata() method.this typically does not
equal the length of the whole byte array.
Datagramsocket
The Datagramsocket represents a connectionless datagram socket.this class
works with the DatagramPacket class to provide for communication using the UDP
protocol . it provides two constructors,the programmer can specify a port to
use or allow the system to randomly use one.
Methods:The most important methods
are -send() and receive().Each takes as an argument an appropriately
constructed Datagrampacket.In the case of the send() method,the data contained in the packet is sent to the
specified host and the port.The receive() method will block the execution until
a packet is received by the underlying socket,at which time the data will be
copied into the packet provided.
Server Program
File name: EchoServer.java
import
java.net.*;
import
java.io.*;
public
class EchoServer{
static
final int serverPort=1026;
static
final int packetSize=1024;
public
static void main(String args[]) throws SocketException{
DatagramPacket
packet;
DatagramSocket
socket;
byte[]
data;
int
clientPort;
InetAddress
address;
String
str;
socket=new
DatagramSocket(serverPort);
for(;;){
data=new
byte[packetSize];
packet=new
DatagramPacket(data,packetSize);
System.out.println("Waiting
to receive the packets");
try{
socket.receive(packet);
}
catch(IOException
ie){
System.out.println("Could
not Receive:"+ie.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
address=packet.getAddress();
clientPort=packet.getPort();
str=new
String(data,0,0,packet.getLength());
System.out.println("Message:
"+str.trim());
System.out.println("From:
"+address);
packet=new
DatagramPacket(data,packetSize,address,clientPort);
try{
socket.send(packet);
}
catch(IOException
ex){
System.out.println("Could
not Send"+ex.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
Client Program
File name: EchoClient.java
import
java.net.*;
import
java.io.*;
public
class EchoClient{
static
final int serverPort=1026;
static
final int packetSize=1024;
public
static void main(String args[]) throws UnknownHostException,SocketException{
DatagramSocket
socket;
DatagramPacket
packet;
InetAddress
address;
String
messageSend;
String
messageReturn;
byte[]
data;
if(args.length!=2)
{
System.out.println("Usage
Error: Java EchoClient <Server name><Message>");
System.exit(0);
}
address=InetAddress.getByName(args[0]);
socket=new
DatagramSocket();
data=new
byte[packetSize];
messageSend=new
String(args[1]);
messageSend.getBytes(0,messageSend.length(),data,0);
packet=new
DatagramPacket(data,data.length,address,serverPort);
System.out.println("Trying
to Send the packet");
try{
socket.send(packet);
}
catch(IOException
ie){
System.out.println("Could
not Send:"+ie.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
packet=new
DatagramPacket(data,data.length);
try{
socket.receive(packet);
}
catch(IOException
iee){
System.out.println("Could
not receive: "+iee.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
messageReturn=new
String(packet.getData(),0);
System.out.println("Message
Returned: "+messageReturn.trim());
}
}
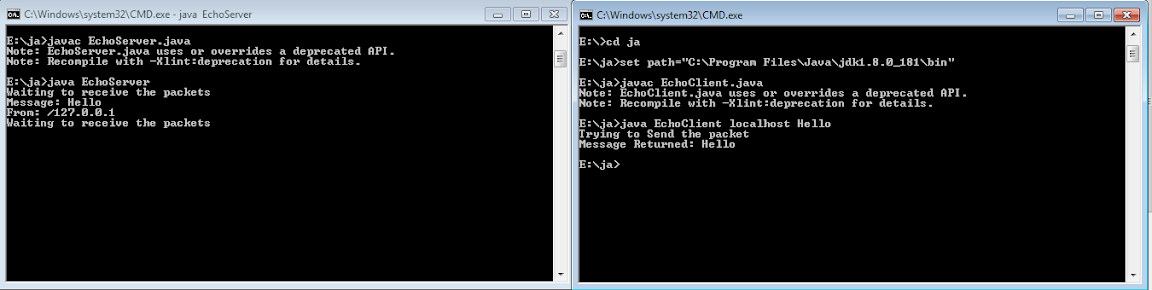
Open Two CMD. Run One Cmd
Server , and another Cmd Client.First Run Server.After Run Client Program.
Output
Before connecting EchoClient , EchoServer Output
After connecting EchoClient , EchoServer and EchoClient Output
URL
URL - Uniform resource locator
Urls to access HTML pages from the Web.
Host Name- The name of the machine on which the resources lives.
File Name-The pathname to the file on the machine.
Port Number- The port number to which to connect
Reference- A Reference to a named anchor within a resource that
usually identifies a specific location within a file
Parsing a URL
The URL class provides several methods that let you query
URL objects.
getProtocol - Returns the protocol identifier component of the URL
getHost-Returns the host name component of the URL
getPort-Returns the port number component of the URL.
getFile-Returns the filename component of the URL
getRef-Returns the reference component of the URL
Parsing a URL
File name: ParseURL.java
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ParseURL{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
URL aURL=new
URL("http://java.sun.com;80/docs/books/tutorial/intro.html#DOWNLOADING");
System.out.println("protocol="+aURL.getProtocol());
System.out.println("host="+aURL.getHost());
System.out.println("filename="+aURL.getFile());
System.out.println("port="+aURL.getPort());
System.out.println("ref="+aURL.getRef());
}
}
Output
Reading from URLConnection
File name: URLConnectionReader.java
import
java.net.*;
import
java.io.*;
public
class URLConnectionReader{
public
static void main(String args[])throws Exception
{
URL
yahoo=new URL("http://www.yahoo.com");
URLConnection
yc=yahoo.openConnection();
BufferedReader
in=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(yc.getInputStream()));
String
inputLine;
while((inputLine=in.readLine())!=null)
System.out.println(inputLine);
in.close();
}
}


0 comments:
Post a Comment